Page 120 - Наукові записки ДПМ. Т 35/2019
P. 120
114 Заморока А.М., Глеба В.М.
by Greater Khingan Mountains on the East. The southern limit of its distribution is
completely unknown. The species presents in Central Asian Mountains: Altai, Tien Shan,
Pamir, which apparently are the nature border for A. leucaspis southward range. The species
is known from south Tajikistan [21] and should be present in North Afghanistan where
restricted by Hindu Kush Mountain Massif from South. The presence of A. leucaspis in North
Iran is doubtful, however it is widespread in neighbor Armenia and Azerbaijan. A. leucaspis
occupies the North of Turkey. Thus, we suggest that A. leucaspis is Euro-Siberian steppic
species.
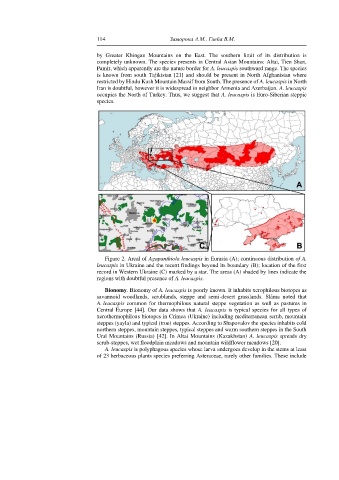
Figure 2. Areal of Agapanthiola leucaspis in Eurasia (A); continuous distribution of A.
leucaspis in Ukraine and the recent findings beyond its boundary (B); location of the first
record in Western Ukraine (C) marked by a star. The areas (A) shaded by lines indicate the
regions with doubtful presence of A. leucaspis.
Bionomy. Bionomy of A. leucaspis is poorly known. It inhabits xerophilous biotopes as
savannoid woodlands, scrublands, steppe and semi-desert grasslands. Sláma noted that
A. leucaspis common for thermophilous natural steppe vegetation as well as pastures in
Central Europe [44]. Our data shows that A. leucaspis is typical species for all types of
xerothermophilous biotopes in Crimea (Ukraine) including mediterranean scrub, mountain
steppes (yayla) and typical (true) steppes. According to Shapovalov the species inhabits cold
northern steppes, mountain steppes, typical steppes and warm southern steppes in the South
Ural Mountains (Russia) [42]. In Altai Mountains (Kazakhstan) A. leucaspis spreads dry
scrub-steppes, wet floodplain meadows and mountain wildflower meadows [20].
A. leucaspis is polyphagous species whose larva undergoes develop in the stems at least
of 23 herbaceous plants species preferring Asteraceae, rarely other families. These include